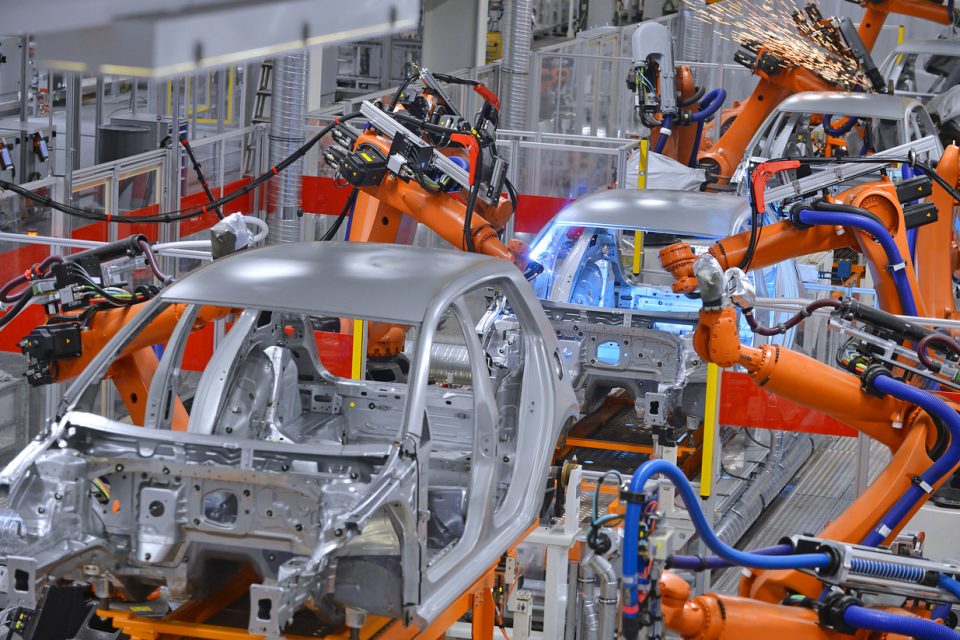
The automotive industry has been using industrial robots for more than half a century, since General Motors first adopted the UNIMATE in the early 1960s. Over the intervening period, the number of robots used in the automation sector has seen massive growth. The technology has improved too with more low cost, flexible, collaborative systems supplementing and replacing cumbersome and inflexible traditional robots.
Using robots allows car and automotive component makers to speed up production, reduce costs, improve quality and protect their workers from harm. Collaborative robots (or ‘cobots’) have created new possibilities for car makers, including the ability to deploy robots in close proximity to human workers without the need for fencing. Cobots allow manufacturers to free workers from dull, dirty and dangerous jobs –plus, cobots are available 24/7, 365.
We will take a look at six examples of cobots being used in the automotive sector, below, but first…
WHERE ARE INDUSTRIAL ROBOTS USED?
There are very few industries that do not benefit from the use of automation. Since the first automotive robot joined the production line at GM, countless other factories and warehouses have adopted robot technologies. Industries that use robots include the pharmaceutical sector, general manufacturing, medical and agriculture. Universal Robots’ cobots are versatile platforms that can be deployed on a wide variety of tasks in several environments. The only limits are payload, safety compliance and your imagination.
WHAT DO INDUSTRIAL ROBOTS DO?
Industrial robots in manufacturing can assume a wide range of jobs from material handling, pick & place and inspection to assembly, packaging & palletizing and finishing applications. Robots are designed to perform repetitive tasks and relieve human workers from strenuous physical labor. Robots can be equipped with machine vision and artificial intelligence systems that enable them to respond to a variety of situations and provide feedback on system performance in real-time.
COBOTS IN AUTOMOTIVE PRODUCTION
Some of the most urgent problems faced by automotive assembly lines include the potential for injury, slow production times, and issues with the quality of the final product(s). These problems can be addressed by deploying cobots.
For example, UR10 robots are used by Ford in Romania to grease camshafts, fill engines with oil and perform quality inspections.
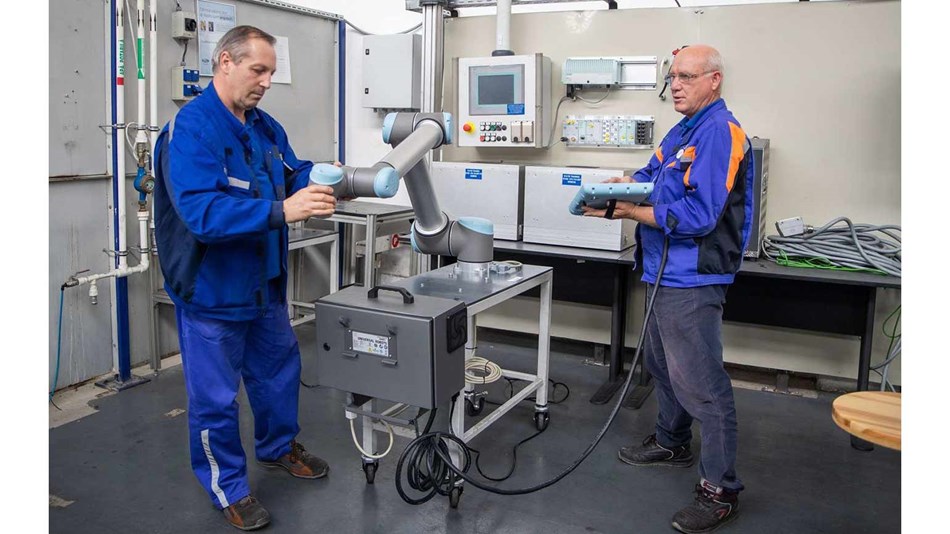

Almost any physical task involved in vehicle construction can be handled by robots. There are also plenty of opportunities for robots to assist with jobs that require decision making, including, for example, performing pass/fail quality inspections to ensure that the final product is of sufficient quality.
WHAT ARE THE 6 MAIN APPLICATIONS FOR COBOTS IN THE AUTOMOTIVE MANUFACTURING SECTOR?
Let’s look at some examples of cobots in automotive production. There are six main types of application. These are assembly, painting, welding, machine tending, material removal and polishing and quality inspection. Before the arrival of cobots, manufacturers needed a different robot to perform each of these tasks. Today, one cobot arm from Universal Robots can perform all of these tasks simply by fitting the right end-effector from the UR+ platform.
Assembly
Cobots perform an important role in many car factories, including assembly. Cobots can handle repetitive tasks on the production line, such as attaching door handles and windshield wipers, which frees human workers to focus on higher value tasks. Cobots with higher payloads, such as the UR16e (payload 16kg/35.3lb) are able to handle larger, bulkier items such as wheels, hatches, and engine hoods.
The Lear Corporation uses flexible, lightweight UR5 cobots to assist with assembling car seats. The UR5 has a small foot print (Ø 149 mm), enabling it to work in tight spaces, where it can perform tasks such as helping to assemble automotive seats and rest frames. At Lear, the UR5 completes a screwdriving action 8,500 times per day, which has optimized the company’s production time. Lear deployed its first UR cobot in 2017 –today the company has 38 UR robots in its Chinese production plant where they are used to perform car seat screw tightening, electrical inspection, pick & place and other important processes.
Painting
Painting robots have become a staple of car manufacturing done by robots. Robots provide consistent painting performance and round the clock availability that no human worker can match. Furthermore, automotive paint is toxic, which poses a major risk to human workers. Tasks, such as applying a perfectly even coat of paint to a large surface are best handled by robots. The precision and performance provided by robots in painting tasks also lowers production costs over time due to less wasted paint and the elimination of human error.
Welding robots
Welding is another dangerous and time-consuming task that is ideally suited to cobots. Cobots can handle Arc, TIG, laser, MIG, ultrasonic, plasma, and spot welding, as well as soldering and brazing. The UR+ platform provides all the hardware and software you need to get started with your automotive welding application. The Olympus UR Welding system, for example, is a low-cost welding solution that’s perfectly suited to small automotive part manufacturers.
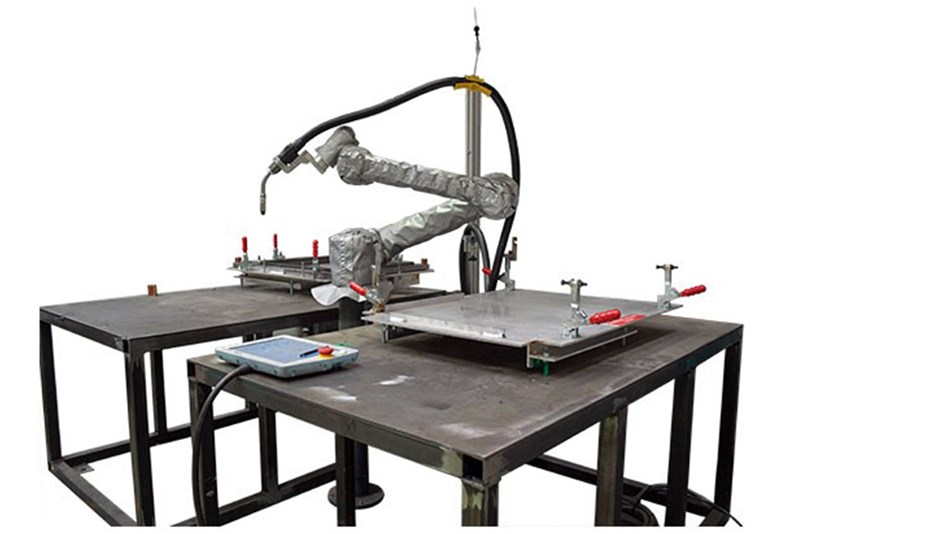

Machine tending
Machine tending is one of those tasks that's ideally suited to collaborative robot-powered automation. Dull, often dirty and sometimes dangerous, it's no surprise that over recent years machine tending has emerged as one of the most popular applications for cobots.
India’s Bajaj Auto is one of the world’s largest motorcycle manufacturers and was the first company in India to deploy cobots. Since then, Bajaj Auto has deployed 100 cobots in its production facilities to assist human workers with machine tending and assembly tasks. This company sought to improve the standardization of their two-wheeler vehicles and increase the speed of production.
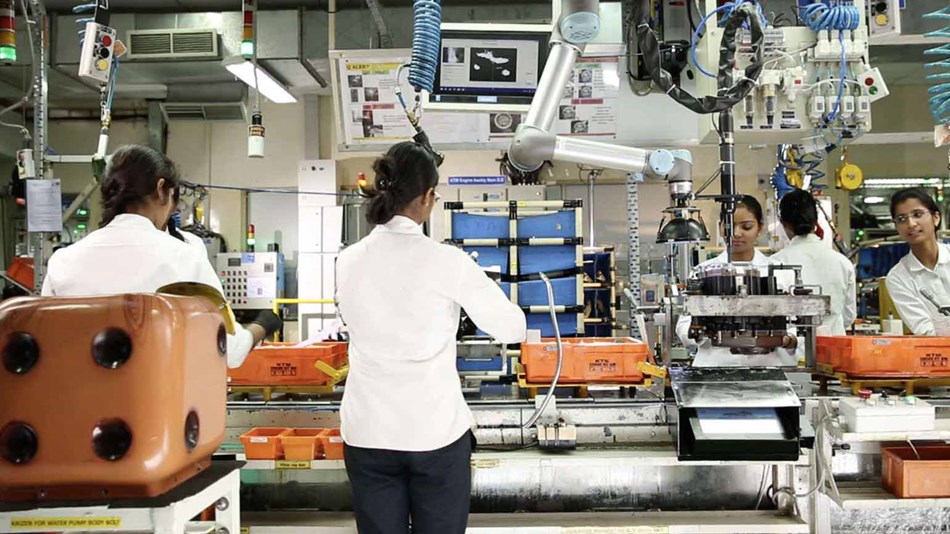

Material removal and polishing robots
Material removal and parts polishing are important processes in vehicle production. These processes includes cleaning up automotive parts along the way by trimming metal or polishing molds for smooth finishes. Like many tasks in car manufacturing, the tasks are repetitive and sometimes dangerous, creating an ideal opportunity for robotic intervention. Material removal tasks include grinding, deburring, milling, sanding, routing and drilling.
Robotiq’s Finishing Kits, for example are hardware and software packages that provide everything manufacturers need to get started on surface finishing, sanding and external tool finishing tasks. The kits include Robotiq’s Finishing Copilot software, which is designed to enable intuitive programming of finishing applications, regardless of the end user’s level of robotics expertise.
UR robots are built to work flexibly alongside human employees, making them a great fit for work cells and production facilities where safety is a priority and space is at a premium.
Quality inspection
Quality inspection processes can make the difference between successful production runs and expensive, labor-intensive failures. Cobots are used by the automotive industry to ensure product quality. UR+ provides a wide variety of hardware and software specially designed to help you automate your automotive quality inspection tasks, including cosmetic optical inspection and metrology.
Indian automotive component manufacturer Craft and Technik Industries (CATI) deployed cobots for inspection and CNC machine tending applications, increasing production and reducing customer rejections to zero along the way. “The time has come for SMEs to automate – robots are no longer the prerogative of large-scale industries only,” said CATI’s CEO, Prashant Shantaram Umbrani. Since deploying the cobots, CATI has managed to achieve a ‘no defect’ production environment and a 20% increase in production.
And Comprehensive Logistics, a manufacturer based in Ohio that specializes in engine assembly, deployed a UR10 collaborative robot equipped with a vision camera to help with inspection tasks. The deployment enabled the Ohio-based contract manufacturer to achieve 100% quality in the sub-assembly of automotive engines.
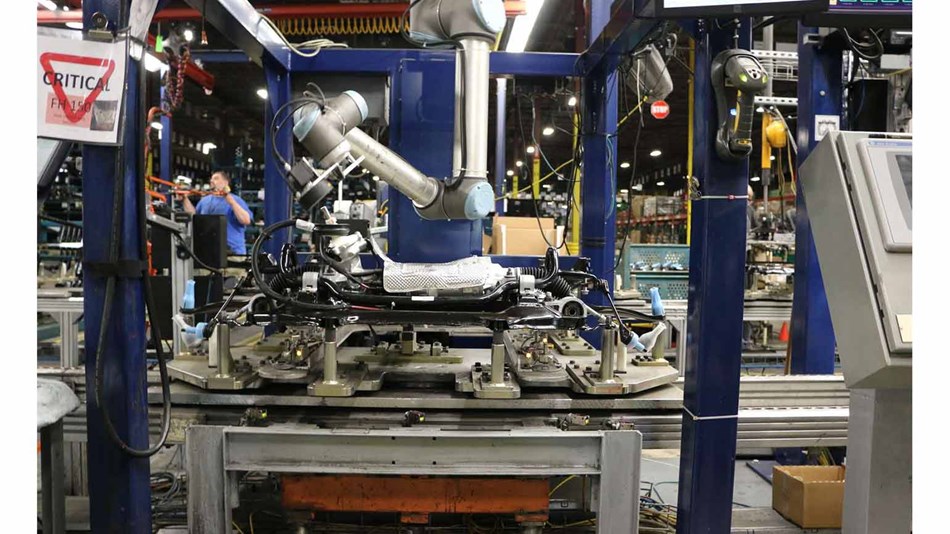

CONTINUED GROWTH IN AUTOMOTIVE MANUFACTURING
There are countless opportunities and applications for robot --and collaborative robot-- intervention in the automotive manufacturing industry. Robots ensure increased quality, lower production times, and fewer workplace injuries.
Universal Robots’ cobots are a popular choice among automotive manufactures due to their flexibility and adaptability. Cobots can be deployed on your factory floor in close proximity to human workers without fencing. And because of their small footprint and easy mobility, automotive manufacturers continue to find new applications for their cobot platforms.
Source: universal-robots.com/blog
