A mechanical seal is a device that helps join systems or mechanisms together by preventing leakage (e.g. in a pumping system), containing pressure, or excluding contamination. The effectiveness of a seal is dependent on adhesion in the case of sealants and compression in the case of gaskets.
A stationary seal may also be referred to as 'packing'.
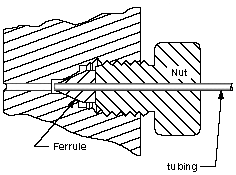
Compression seal example
Seal types:
- Induction sealing or cap sealing
- Adhesive, sealant
- Bodok seal, a specialized gas sealing washer for medical applications
- Bonded seal, also known as Dowty seal or Dowty washer. A type of washer with integral gasket, widely used to provide a seal at the entry point of a screw or bolt
- Bridgman seal, a piston sealing mechanism that creates a high pressure reservoir from a lower pressure source
- Bung
- Compression seal fitting
- Diaphragm seal
- Ferrofluidic seal
- Gasket or Mechanical packing
- Flange gasket
- O-ring
- O-ring boss seal
- Piston ring
- Glass-to-metal seal
- Glass-ceramic-to-metal seals
- Heat seal
- Hose coupling, various types of hose couplings
- Hermetic seal
- Hydrostatic seal
- Hydrodynamic seal
- Inflatable seal Seals that inflate and deflate in three basic directions of operation: the axial direction, the radial-in direction, and the radial-out direction. Each of these inflation directions has their own set of performance parameters for measurements such as the height of inflation and the center-line bend radius that the seal can negotiate. Inflatable seals can be used for numerous applications with difficult sealing issues.
- Labyrinth seal A seal which creates a tortuous path for the liquid to flow through
- Lid (container)
- Rotating face mechanical seal
- Face seal
- Plug
- Radial shaft seal
- Trap (plumbing) (siphon trap)
- Stuffing box (mechanical packing)
- Wiper seal
- Dry gas seal
Source: wikipedia.org
