
In its latest report on the collaborative robot market, Interact Analysis has revised downwards the growth predictions made in our 2019 report. The main factor behind this downward revision is, of course, the COVID-19 pandemic, but there are other downward drivers, such as competition from small articulated and SCARA robots in industrial settings, and a slower than expected increase in cobot installations in non-industrial settings. Nevertheless, this report gives good grounds for optimism for the short to medium term in the collaborative robot sector.
V-shaped rebound and sustained growth predicted
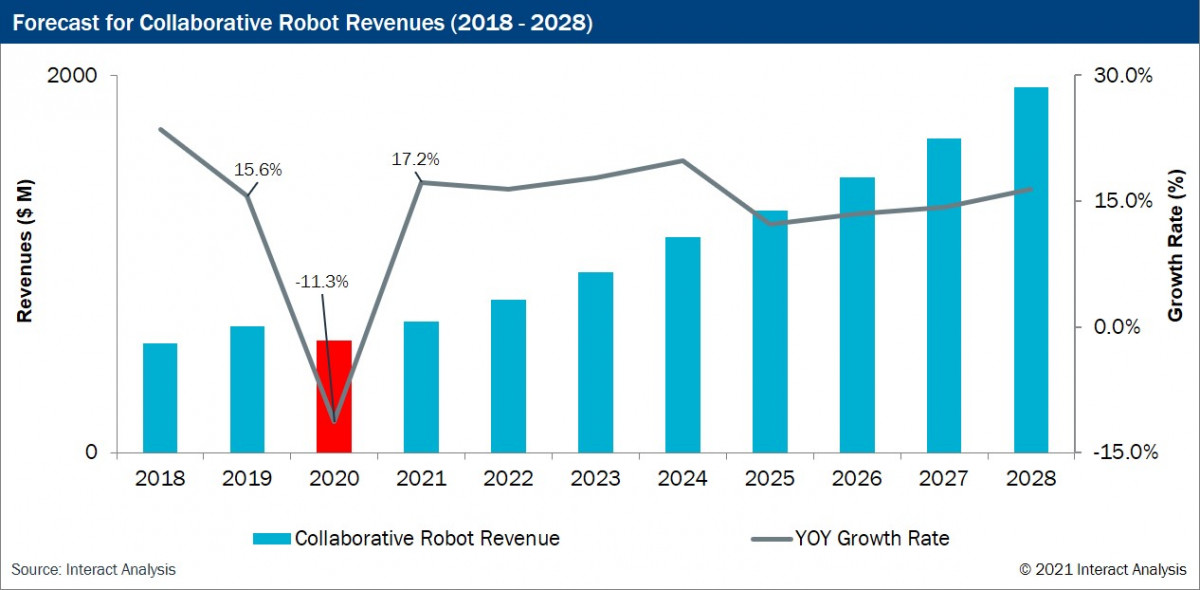
The collaborative robot market weathered a difficult 2019 due to a slow-down in the global economy which affected the important Asian market the most, and a tumultuous 2020, when the market saw negative growth for the first time – -11.3% in revenue terms, and -5.7% in shipment terms. Factory and warehouse shut-downs slowed down demand and customers exercised caution with investment, leading to delays and cancellations of orders. However, Interact Analysis’s in-depth research has found chinks of light for the sector. The company predicts that there will be a V-shaped rebound for the industry which will result in growth of nearly 20% in 2021, surpassing the 2019 market size. Thereafter up to 2028 there will be an annual growth rate of the order of 15-20%. Not as high as previously predicted, but healthy nonetheless.
A concept in evolution
It’s not been long since the birth of collaborative robots, and the concept of “collaboration” alone doesn’t necessarily attract investors. But in a short space of time they have evolved from being a “conceptual” product to being a “strategic” one. Suppliers have gradually moved from simply selling the concepts of “collaboration” or “safety” to marketing specific landing solutions in different application scenarios and service areas. For instance, in the field of industrial manufacturing, with the application of high-precision sensors, machine vision, end arm tools and safety control (alarm) software, flexible production and cooperation between human and robot can be realized. Moving forward, there is the potential to partially replace or assist manual work in the processes of picking, placing, loading and unloading, palletizing, packaging, quality inspection and other operations.
In the service field, with the deepening of machine vision and machine learning, the application of robots in education, medical care, logistics, catering, retail and other service industries is also increasing. Whether collaborative robots have enough competitiveness in this respect is one of the key factors to determine the market’s future growth rate.
Market forecast: flexibility and innovation are the main drivers
In terms of market growth, collaborative robots have been trail-blazers in the robotics industry. In 2019, global cobot revenues totalled $669.9 million, a 15.6% increase on 2018; 22,459 cobots were shipped, up 18.8% year-on-year, pretty good going in the context of a sharp decline in the overall market for robots.
Notwithstanding the sucker-punch the collaborative robot market took in 2020, the potential market size is still large; the key to further growth lies in infiltrating new application scenarios (both manufacturing and non-manufacturing applications) and in technological breakthroughs. The industry is up and running in these respects. Interact Analysis forecasts that annual cobot revenues will reach $1.94 billion in 2028, accounting for 15.7% of the total robot market.
Flexibility and ease of use are the main competitive advantages of collaborative robots in industrial applications. Although most of the new products released in the last 18 months are in the payload range of 0-9kg, many companies have produced cobots with larger payloads. The main barrier for larger payload cobots is that the speed of operation has to be reduced to enable safe functioning around humans. Additional sensors, software algorithms and peripherals can be added to improve the speed and safety of these larger robots but this comes at a higher overall cost. Interact Analysis predicts that <5kg and 5-9 kg cobots will still account for the majority of sales in 2024, with a total of 80.3% revenue share and 85.1% shipment share. In industrial applications and non-manufacturing fields, safety, speed, accuracy and cost issues mean that smaller payload models are more competitive.
10-20kg cobots have seen some increased demand from the logistics and plastics and rubber industries. However, shipments of these models are still relatively low, and the applicability for >20kg cobots is limited.
Key end-industries for collaborative robots
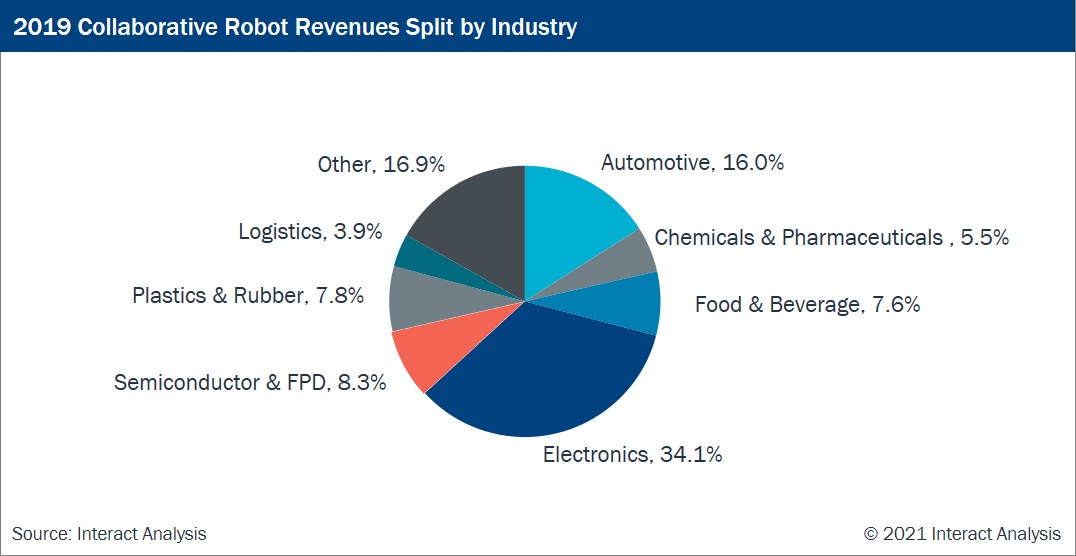
Collaborative robot manufacturers are striving to develop technologies suited to more and more manufacturing settings so as to increase cobot market growth potential. However, we have concluded that during the forecast period, electronics and automotive will remain the two largest end-industries. Together, they occupied half of the market share in 2019. But the barriers in these two industries are relatively high and it is difficult for new entrants to gain a foothold. On the other hand, service scenarios can be regarded as a potentially lucrative market for new entrants. In warehousing and logistics, health care, smart retail and other emerging industries, the safe and flexible characteristics of collaborative robots are very attractive.
Most common applications
Material handling, assembly and pick & place are forecast to remain the three biggest uses of collaborative robots. These three functions which accounted for 71.9% of collaborative robot revenues in 2019 will hold a 62.7% share in 2024.
Pick & place and assembly processes are usually small payload but repetitive tasks, inherently requiring greater accuracy and precision and typically a vision system to aid this. Traditional SCARA and small payload six-axis robots can also be effective. The advantage of collaborative robots is the faster ROI and the ability to work side by side with workers.
Machine tending (included within the material handling category) is one of the biggest current uses of collaborative robots. Machine tending applications are by nature highly repetitive and sometimes more dangerous for humans and here the use of cobots is highly advantageous.
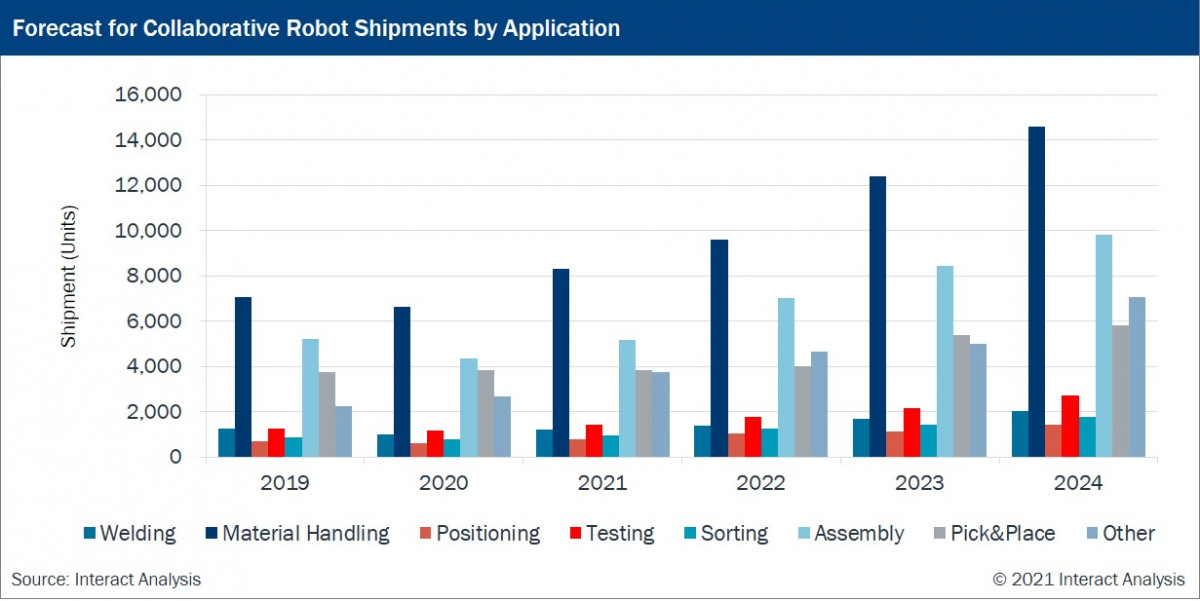
By 2024, Interact Analysis forecasts the continuing emergence of pick and place as the third biggest application for collaborative robots, but note the bar on the far right of each graph, denoting ‘other applications’. There is clearly evidence that innovative cobot technologies are poised to penetrate a range of new manufacturing and non-manufacturing scenarios – settings for which industrial robots are unsuited.
Regional perspective: Over half of cobots were shipped to Asia in 2019, but change is afoot
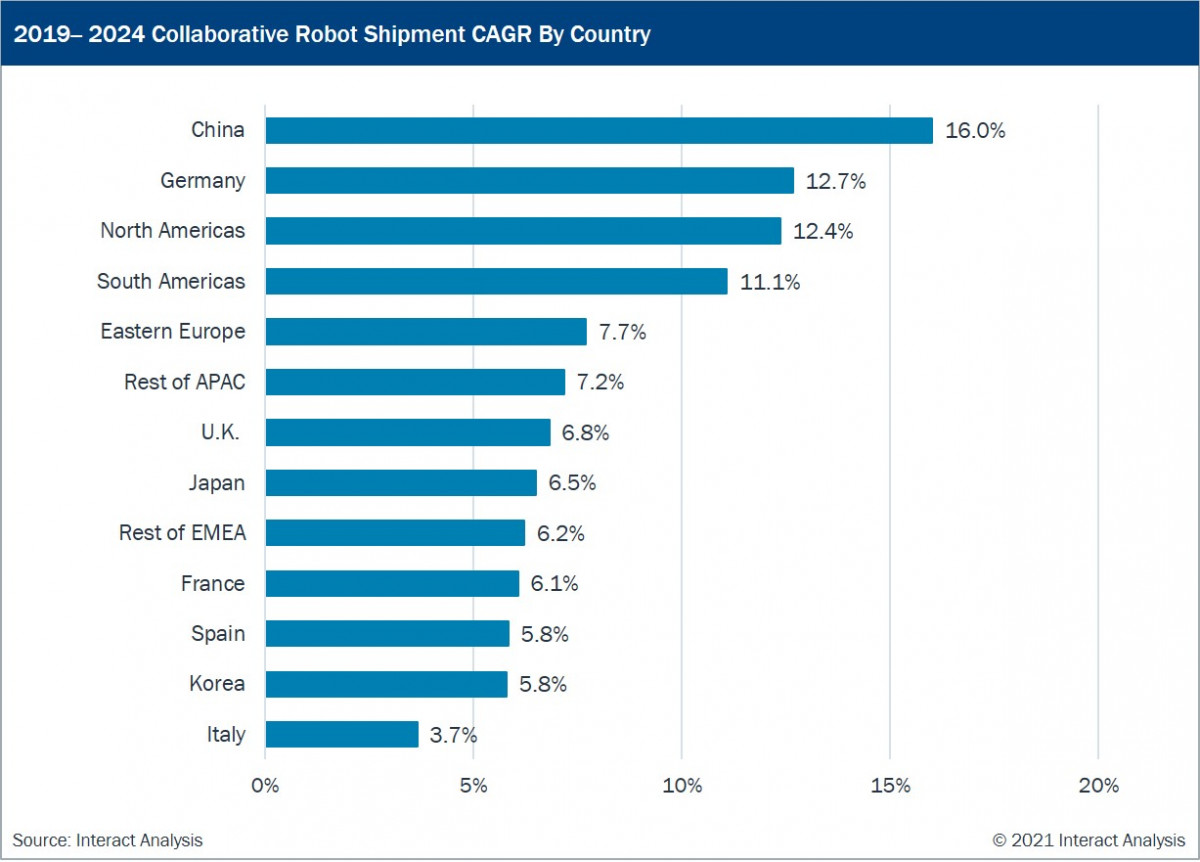
China, Germany, North America and the South Americas are predicted to be the biggest markets for cobot shipments over the next 5 years, with revenues growing at a CAGR of over 10% in each of those regions. Interestingly, the reasons why collaborative robots are an attractive proposition vary from region to region. End-users in China, APAC and Eastern Europe are attracted by their relatively low upfront costs, ease of installation and ease of use. Small and medium sized companies use collaborative robots to increase automation efficiency, mainly in labour-intensive industries such as electronics.
In Europe and North America, the safety features of cobots have received a lot of attention and are a focus for product development. In 2019, the three biggest end-users in North America were automotive, electronics and the plastic & rubber industry. By 2024, although the automotive industry will continue to lead the field and will account for more than 25% of revenues, collaborative robots will make serious inroads into the chemical & pharmaceutical and food & beverage sectors, surpassing cobot sales to the plastics & rubber industry, and almost outstripping sales to the electronics industry. Non-manufacturing usage is also emerging in the US.
In Japan and South Korea, due to the aging population and a shortage of labour, the ability of collaborative robots to work alongside human beings represents a unique selling point.
Fertile ground for small innovators
In the final section of their collaborative report, Interact Analysis profiles a lengthy list of cobot companies. Whilst the list inevitably details the big players such as Mitsubishi Electric and Kawasaki, what is striking is the plethora of relatively recent start-ups such as AUBO Robotics based in Tennessee, USA. Employing in the region of 100 people, the company was founded with the original name ‘Smokie Robotics’ 6 years ago by three professors from the US and China. One product is described as follows in the profile: AUBO Robotics collaborative robot AUBO-series are a six-axis, 3, 5, 7, and 10kg payload with 625 to 1350 mm reach lightweight industrial robots made for human-centric agile manufacturing. An intriguing description which somehow sums up the potential of cobotics.
Source: roboticstomorrow.com
